DBS Bank India, in partnership with CRISIL, has published the third installment of its ‘Women and Finance’ series. This report, based on a survey of 400 self-employed women from 10 major Indian cities, offers a deep dive into their entrepreneurial journeys.
The study explores various aspects of their businesses, including funding sources, banking practices, digital payment preferences, workforce management, and sustainability initiatives. It also addresses challenges like gender bias and examines how age, income, and location influence their business decisions. The report highlights key areas where women entrepreneurs need support and identifies opportunities for enhancing their business capabilities.
Sources of business funding:
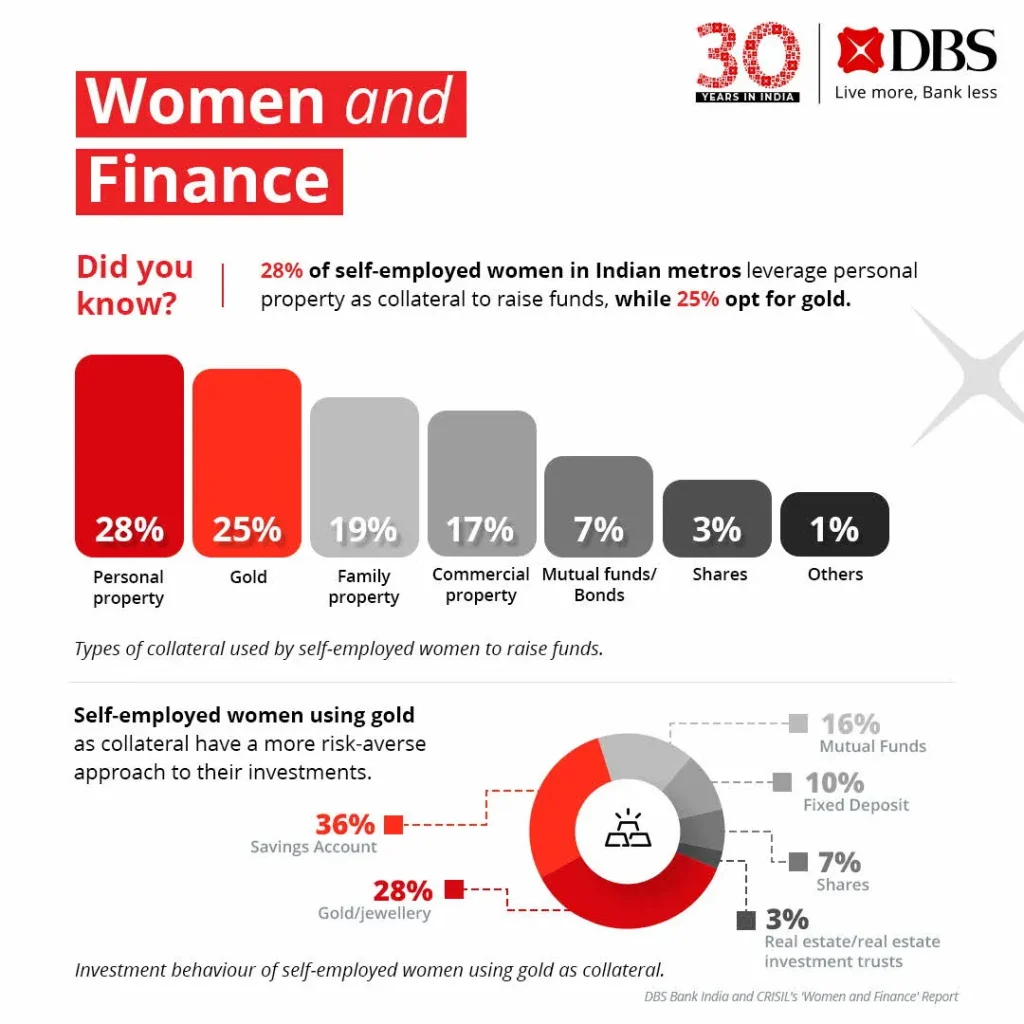
65% of self-employed women in Indian metros have not taken a business loan, with 39% relying on personal savings to fund their enterprises. Among those who have obtained loans, bank loans were the primary choice, preferred by 21%. Women entrepreneurs often use personal assets for collateral, with 28% leveraging personal property and 25% turning to gold—reflecting their risk-averse approach to investments. 64% of respondents who use gold as collateral predominantly invest in safer options like savings accounts and gold.
Awareness of government schemes:
The survey revealed a significant awareness gap regarding government schemes, with 24% of respondents indicating they were unaware of available options. Additionally, 34% stated they had not utilised any government scheme for their businesses. To bridge this gap, the DBS Foundation has launched a robust training program in partnership with Haqdarshak to boost financial literacy and empower women to access government entitlements and financial services. The program targets 200,000 marginalised beneficiaries, with women comprising 80% of the participants.
Banking products:
39% of women entrepreneurs use cash credit (CC) and overdraft (OD) facilities, followed by corporate credit cards (25%) and property-backed term loans (11%). 39% of respondents cited competitive interest rates and flexible repayment terms as key factors influencing their choice of bank for loans.
Support beyond financial assistance:
Beyond financial support from banks, women entrepreneurs expressed a desire for mentorship (26%), support in navigating government schemes (18%), and assistance in digitalising financial processes (15%). In terms of business enablement, 18% were interested in women-based communities, and 13% sought access to industry-specific financial data and benchmarks.
Commenting on the report, Divyesh Dalal, Managing Director & Head – Global Transaction Services, SME and Institutional Liabilities, DBS Bank India, said, “The insights from our latest ‘Women and Finance’ report highlight key areas where we can make an impact. We see opportunities to boost awareness and adoption of government entitlements through education and training. Additionally, it underscores the need to build entrepreneurial ecosystems with networking platforms and communities that foster collaboration, mentorship, skill-building, and knowledge exchange to accelerate growth for women in business. DBS Bank India goes beyond traditional banking to support entrepreneurs and be a trusted partner for SMEs and startups. We will continue working with partners like CRISIL to better understand and empower women in their entrepreneurial journeys, backed by data-driven insights.”
The bank has leveraged insights from the report to design a customised proposition for women entrepreneurs, working closely with its ecosystem partners. Through its partnership with Zaggle, DBS Bank India will offer exclusive benefits, such as discounts on Zaggle EMS, a tool that streamlines expense management. Women entrepreneurs will also receive a reduction in card issuance fees and service charges for Zaggle’s payment and tax solutions will be waived off. Additionally, through its partnership with FundEnable, the bank will organise capacity-building activities, including a knowledge series and bootcamps on fundraising, market strategies, and pitch enhancement. The bank has also partnered with India Accelerator, a fund-led startup accelerator from Gurgaon to curate special offers on co-working spaces and accelerator programs for women entrepreneurs.
Trends in digital payments:
UPI has played a pivotal role in digitising India’s financial transactions. According to the Reserve Bank of India, the share of UPI in digital payments reached close to 80% in fiscal 2024. UPI leads in the payment of business expenses, followed by mobile banking.
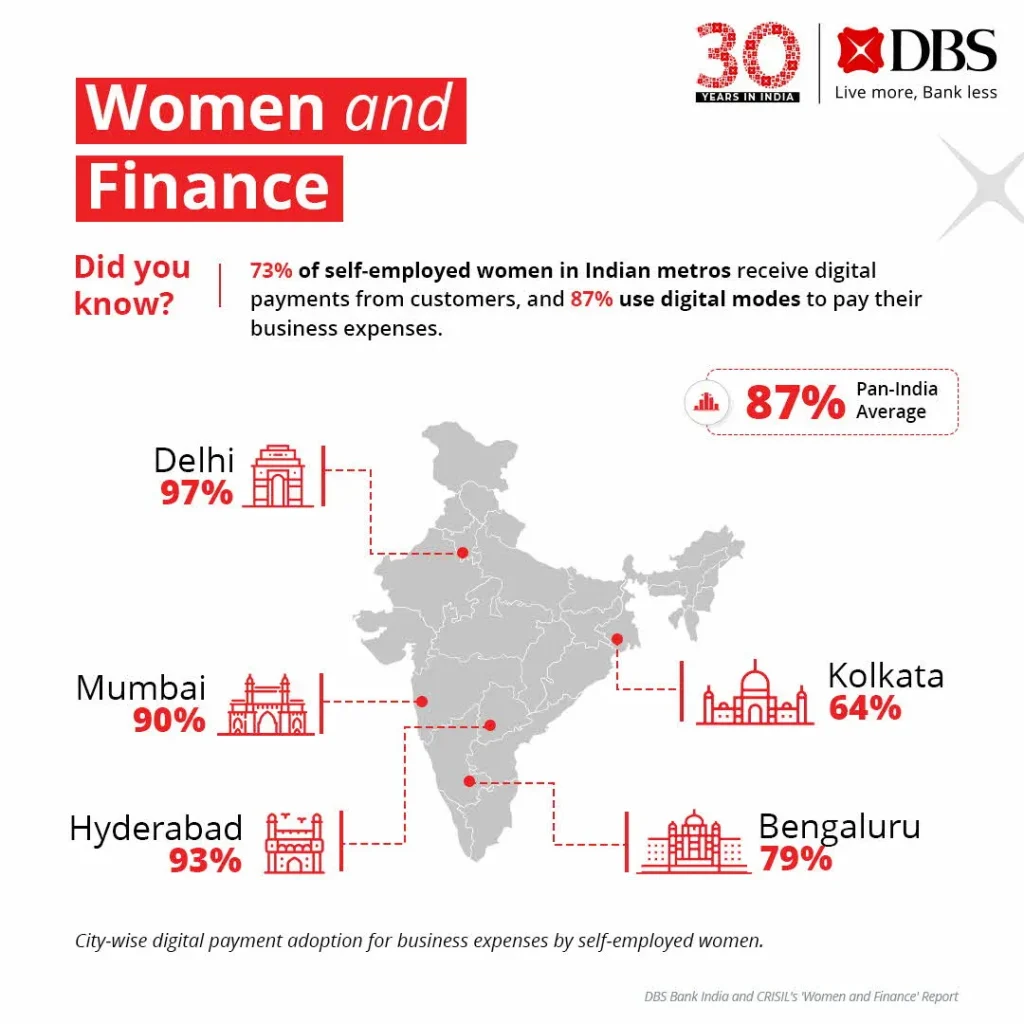
Pushan Sharma, Director-Research, CRISIL Market Intelligence & Analytics, said, “73% of self-employed women surveyed preferred receiving payments from customers digitally, and 87% used digital methods to pay their business expenses. UPI is the most-used mode for both receiving (35%) and paying (26%) business expenses. However, cash remains indispensable for payroll and operational expenses, used by 36% of respondents.”
Adopting sustainable business practices:
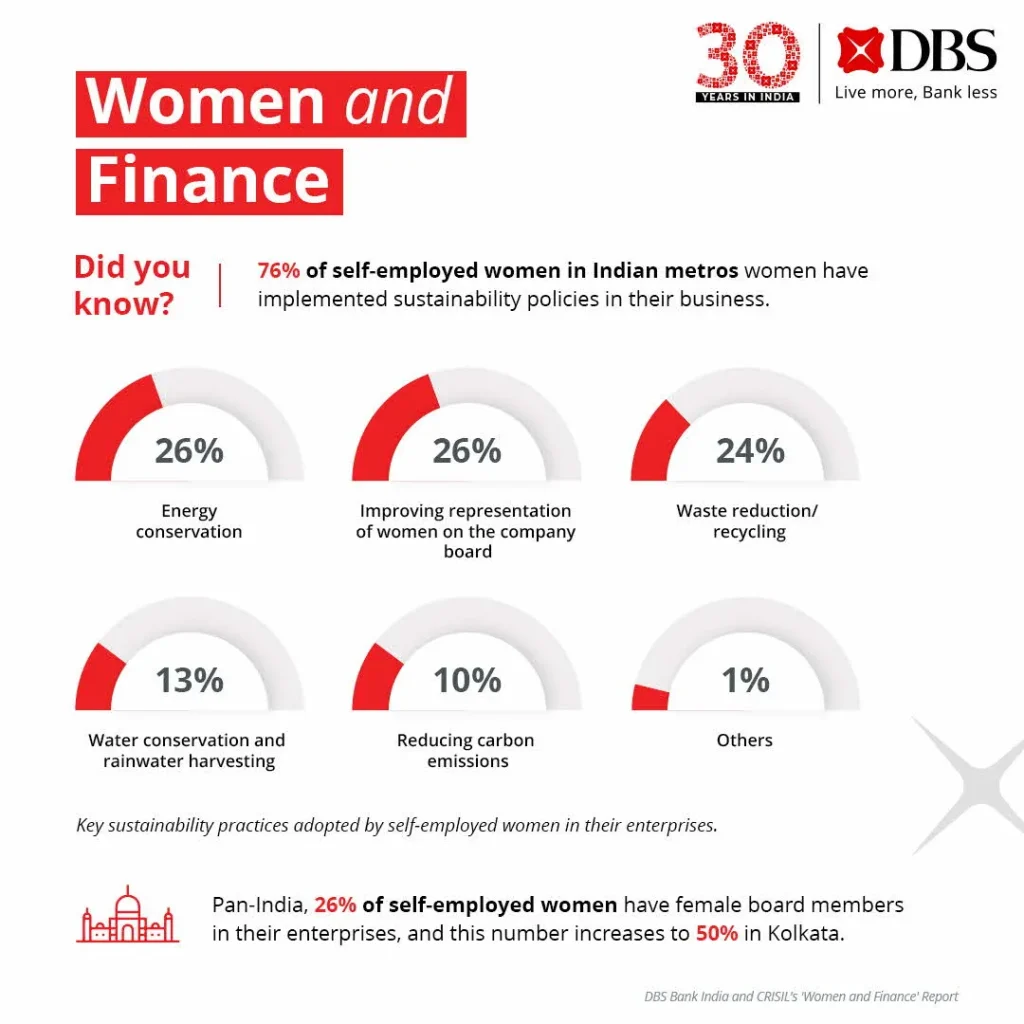
The insights underscore a growing trend toward sustainability. 52% of self-employed women in Indian metros have implemented sustainability policies in their businesses, while 14% have approached a bank for sustainability-linked finance. Encouragingly, 76% have implemented sustainable business practices, such as energy conservation, incorporating female representation on their boards, and waste reduction and recycling measures. 26% of respondents prioritise energy conservation efforts, while 24% focus on waste reduction and recycling. Additionally, 26% of self-employed women have female members serving on their boards, reflecting their commitment to gender diversity and inclusion. 13% have adopted practices related to water conservation and rainwater harvesting.
DBS Bank India aims to support holistic financial management for women, guided by insights from the Women and Finance study. This underscores how DBS embodies being a different kind of bank, enabling customers to ‘Live More, Bank Less’ in line with its brand promise. The first report released in January 2024 focused on savings, investment patterns, and behaviors among salaried and self-employed women in urban India. The second report, launched in March 2024, explored career progression, workplace policy preferences, and challenges faced by women in the workforce.











